Pulmonary
Improved quality of life – physical, emotional and occupational well-being Medical regimens customized to patients’ individual needs, possibly reducing overall dependence on medications Reduced medical cost Reduced dependence on the medical system.
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure how well the lungs take in and release air and how well they move gases such as oxygen from the atmosphere into the body’s circulation.The tests can determine the cause of shortness of breath and may help confirm lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis or emphysema. The tests also are performed before any major lung surgery to make sure the person won’t be disabled by having a reduced lung capacity.
Lung volume measurement detects restrictive lung diseases. In this set of diseases, a person cannot inhale a normal volume of air. Restrictive lung diseases may be caused by inflammation or scarring of the lung tissue (interstitial lung disease) or by abnormalities of the muscles or skeleton of the chest wall.Testing the diffusion capacity (also called the DLCO) permits an estimate of how efficiently the lungs transfer oxygen from the air into the bloodstream.
Testing your lungs can help doctors diagnose lung diseases such as:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Damaged or scarred lung tissue
Disease caused by breathing in asbestos fibers
collection of inflammatory cells around organs
Infections
Thickened, stretched, or enlarged airways
Thickening or hardening of your connective tissues
Weakness of the muscles in the wall of the chest
This is one of the most common pulmonary function tests. Spirometry measures how much air you can breathe in and out. It also measures how fast you can empty the air out of your lungs.
Spirometry helps diagnose breathing problems such as asthma and COPD
The most air you can breathe out after inhaling deeply. The results will let you know if you’re less able to breathe normally.
How much air you can exhale in 1 second. The score tells your doctor how severe your breathing problem is.
Smokers, bio fuel users and people exposed to air pollution are at highest risk of developing COPD. Since COPD is potentially progressive and fatal disease, early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
Forced vital capacity (FVC). This is the amount of air exhaled forcefully and quickly after inhaling as much as you can.
Forced expiratory volume (FEV). This is the amount of air expired during the first, second, and third seconds of the FVC test.
Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR). This is the fastest rate that you can force air out of your lungs.
maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) .Formerly referred to as maximum breathing capacity, is a pulmonary function test (PFT) that measures the maximum amount of air a person can inhale and then exhale with voluntary effort
We are the one of the first day care clinic in Ahmedabad having DLCO machine.
The DLCO measures the ability of the lungs to transfer gas from inhaled air to the red blood cells in pulmonary capillaries.
For the of early cases Lung Fibrosis and Pulmonary hypertension
What does low DLCO indicate?
A low DLCO indicates
a loss of vasculature,
as seen in COPD;
or pulmonary vascular disease (ie, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
What does a high DLCO mean?
A high DLCO on a PFT is most frequently associated with
large lung volumes,
obesity, and
asthma.
Other conditions are much less common. A clinical condition, which typically reduces DLCO, may deceptively normalize DLCO in such patients.
Emergency Care
consectetur adipisicing elit.
Operation Theater
consectetur adipisicing elit.
Outdoor Checkup
consectetur adipisicing elit.
Cancer Service
consectetur adipisicing elit.
Blood Test
consectetur adipisicing elit.
Pharmacy
consectetur adipisicing elit.
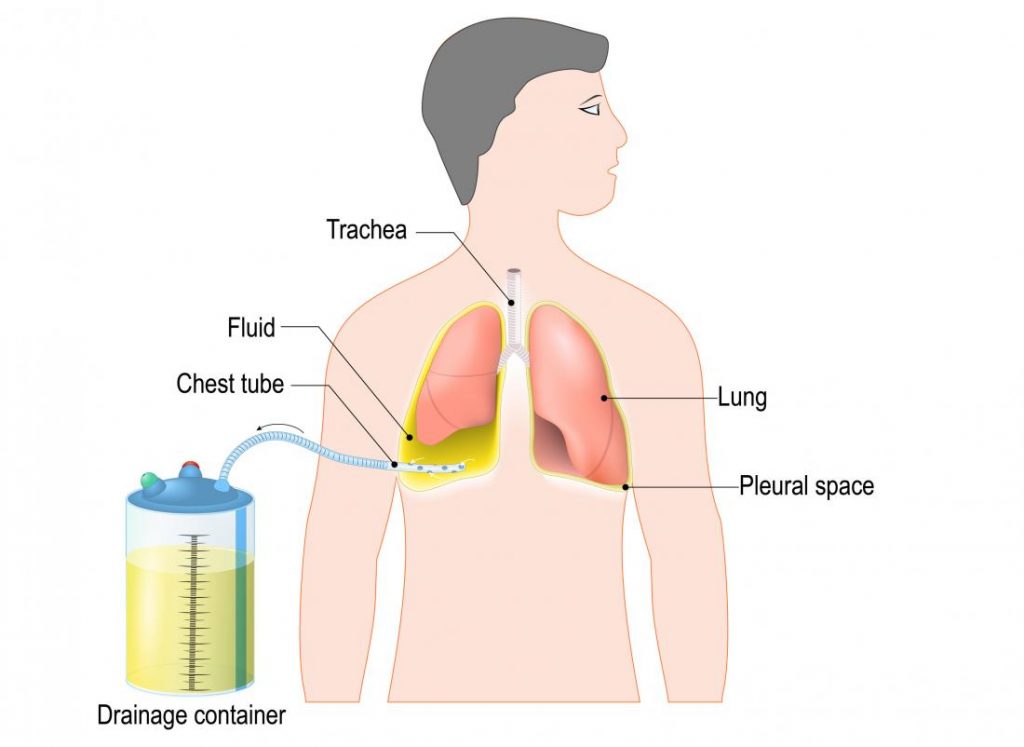
Intercostal Chest Drain Insertion (Tube Thoracostomy)
Indications
- Pneumothorax : Open or closed; simple or tension
- Hemothorax
- Hemopneumothorax
- Hydrothorax
- Chylothorax
- Empyema
- Pleural effusion
- Palliation of breathlessness in malignant pleural effusions
- To facilitate pleurodesis
Contraindications
- The need for emergent thoracotomy is an absolute contraindication to tube thoracostomy.
- Relative contraindications include the following:
- Coagulopathy
- Pulmonary bullae
- Pulmonary, pleural, or thoracic adhesions
- Loculated pleural effusion or empyema
- Skin infection over the chest tube insertion site
During a chest tube insertion, the doctor must work around several major organs, including the lungs and heart. Potential complications include:
- excessive bleeding
- infection
- injuries to the heart, blood vessels, arteries, or lungs
- perforation (puncturing) of the diaphragm
- punctured lung
OUR
DEPARTMENTS
- Intercostal Chest Drain Insertion (Tube Thoracostomy)
- Pulmonary Function Testing
- Pleurocentesis/Thoracentesis
- Skin Prick Allergy Testing
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation
- Sleep Study or Polysomnography
- Medical Thoracoscopy
- Bronchoscopy
Chest Tube Removal
Doctors remove chest tubes when they are no longer necessary, for example when the tube is no longer draining blood or fluid.
They will also remove the tube if it becomes blocked or is not working correctly.
Recovery
Ideally, a person’s symptoms will improve following the use of a chest tube.
People should monitor the incision site for signs of infection while it heals, and inform their doctor as soon as possible if the wound swells, turns red, or starts oozing pus. It is likely that a small scar will remain at the insertion site.
Outlook
A chest tube can be a relatively non-invasive way to access the pleural space to drain fluid or administer medication.
Sometimes, if the chest tube does not resolve a person’s problem, they may need more invasive surgery.
After chest tube removal, a person should follow a doctor’s recommendations on how to care for the incision site.
We’re Trusted & Largest Senior Care Home
