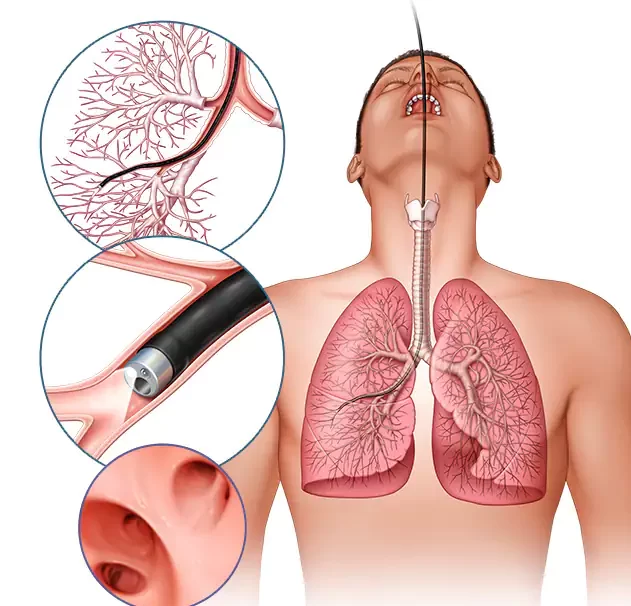
Bronchoscopy
Home > Departments
Bronchoscopy
is a painless, direct examination of your air passages. It may be used to gather specimens, to diagnose tumors, and to find and remove foreign objects in the lungs. A bronchoscope is a flexible tube with a Powerful light source and optical lenses. Bronchoscopy is performed by specially trained physicians, including pulmonary medicine specialists.
Why it's done
Bronchoscopy is usually done to find the cause of a lung problem. For example, your doctor might refer you for bronchoscopy because you have a persistent cough or an abnormal chest X-ray.
Reasons for doing bronchoscopy include:
Diagnosis of a lung problem
Identification of a lung infection
Biopsy of tissue from the lung
Removal of mucus, a foreign body, or other obstruction in the airways or lungs, such as a tumor
Placement of a small tube to hold open an airway (stent)
Treatment of a lung problem (interventional bronchoscopy), such as bleeding, an abnormal narrowing of the airway (stricture) or a collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
Bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is a procedure that is sometimes done during a bronchoscopy. It is also called bronchoalveolar washing. BAL is used to collect a sample from the lungs for testing. During the procedure, a saline solution is put through the bronchoscope to wash the airways and capture a fluid sample.
These tests help diagnose different disorders of the lungs including:
Bacterial infections such as tuberculosis and bacterial pneumonia, Fungal infections, Lung cancer
Why bronchoscopy and BAL is require?
if you have symptoms of a lung disease, such as: Persistent cough, Trouble breathing, Coughing up blood
Transbronchial lung biopsy (TBB) is a procedure performed during flexible bronchoscopy with the use of biopsy forceps. Usually, the purpose is to obtain samples of peripheral lung tissue in order to diagnose interstitial lung disease or to specify the character of a peripheral lung lesion
Why Transbronchial lung biopsy is require?
A transbronchial biopsy is most often performed when there is diffuse infiltrative pulmonary disease, tumors, rejection of a transplanted lung, or severe illness that prevents the use of open lung biopsy.
Bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy (BLC) is a novel bronchoscopic technique of obtaining lung biopsy . It involves the bronchoscopic placement of a flexible cryoprobe inside the lung parenchyma, freezing the probe and shearing out the lung tissue frozen around the tip.
The idea of debulking surgery is to safely remove as much cancer as possible. The remaining cancer is usually treated with other therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiation.
EBUS (endobronchial ultrasound) bronchoscopy is a procedure used to diagnose different types of lung disorders, including inflammation, infections or cancer. Performed by a pulmonologist, EBUS bronchoscopy uses a flexible tube that goes through your mouth and into your windpipe and lungs.
Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is a minimally invasive but highly effective procedure used to diagnose lung cancer, infections, and other diseases causing enlarged lymph nodes in the chest.
This is the fastest rate that you can force air out of your lungs.
Rigid Bronchoscopy is a procedure used to gain access to the patient's airway and allows the passage of larger airway instruments and cameras to diagnose and treat airway disease. This form of bronchoscopy is done by highly trained specialists.
When is a rigid bronchoscopy used?
Rigid bronchoscopy is most commonly used to manage patients who have obstruction of either their trachea or a proximal bronchus, since the rigid bronchoscope's large lumen facilitates suctioning and the removal of debris, or for interventional procedures such as insertion of airway stents
Tracheobronchial stenting refers to the placing of a stent in a patient's airways to treat or prevent restricted airflow. The procedure is minimally invasive and is most often used to relieve symptoms caused by cancerous tumours blocking airway
A stent can be used to stabilize the cricoid plate once it has been divided anteriorly or posteriorly, with or without cartilage placement, to keep the complex in an expanded formation during healing. Stenting to help stabilize the laryngeal structure normally lasts for 2-6 weeks
Why would you need a stent in your lung?
Tracheobronchial (airway) stents are devices used to splint narrowed airways open. Narrowed, or stenotic, airways result from abnormal granulation tissue, lung cancer, metastatic cancers, infections, tuberculosis, lymphoma or other inflammatory diseases.
flexible bronchoscopy is more widely available and most pulmonary physicians are trained in its use so it can be used to remove such foreign bodies.
The most common symptoms of foreign-body aspiration are coughing, choking, and wheezing. Fever, stridor, chest pain, and throat or sternal discomfort occur less frequently. Laryngotracheal foreign bodies present with cough, stridor, hoarseness, and increased respiratory effort.
What happens if a foreign object gets in your lungs?
If you breathe a foreign object into your nose, mouth, or respiratory tract, it may become stuck. This can cause breathing problems or choking. The area around the object also can become inflamed or infected.
maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) .Formerly referred to as maximum breathing capacity, is a pulmonary function test (PFT) that measures the maximum amount of air a person can inhale and then exhale with voluntary effort.
We are the one of the first day care clinic in Ahmedabad having DLCO machine.
The DLCO measures the ability of the lungs to transfer gas from inhaled air to the red blood cells in pulmonary capillaries.